搜索结果: 1-12 共查到“大气化学 PM2.5”相关记录12条 . 查询时间(0.087 秒)

近日,中国科学院城市环境研究所大气污染控制化学研究组(陈进生研究团队)发表重要成果:“利用二次有机示踪物直观的反映沿海城市二次有机气溶胶的主要来源和形成机制”。研究成果以“Characteristics of PM2.5-bound secondary organic aerosol tracers in a coastal city in Southeastern China: seasonal...
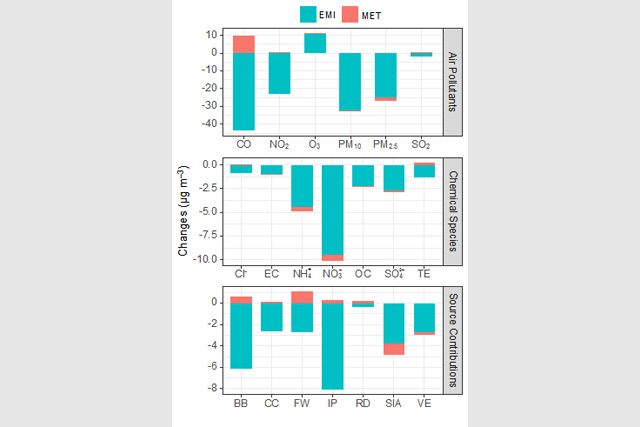
日前,我校环境学院大气科学系孔少飞教授团队与湖北省环境监测中心站等合作开展的研究《由于新型冠状病毒肺炎武汉封城后大气PM2.5化学组成和来源发生了显著变化》在《全环境科学》在线发表,这也是双方首次以湖北省大气复合污染研究中心共同发表的论文。第一作者为2017级博士研究生郑煌,通讯作者为孔少飞教授。为阻断新冠病毒传播,武汉在2020年1月23日采取“封城”措施,为扼制疫情扩散做出了重大贡献。“封城”...
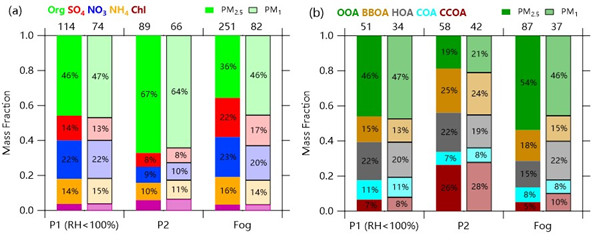
中科院大气物理研究所孙业乐课题组联合暨南大学团队于2018年秋冬季在河北固城开展了一次综合观测(细颗粒物平均浓度:124±95μgm-3)。观测期间利用最新的飞行时间气溶胶化学组分监测仪(ToF-ACSM)和PM1/PM10自动切换系统对PM1和PM2.5的化学组分进行了实时在线测定和分析。此次综合观测具有典型的代表性,特别是整个观测根据气象条件差异可以分为明显两个不同阶段,第一阶段(P1)伴随高...
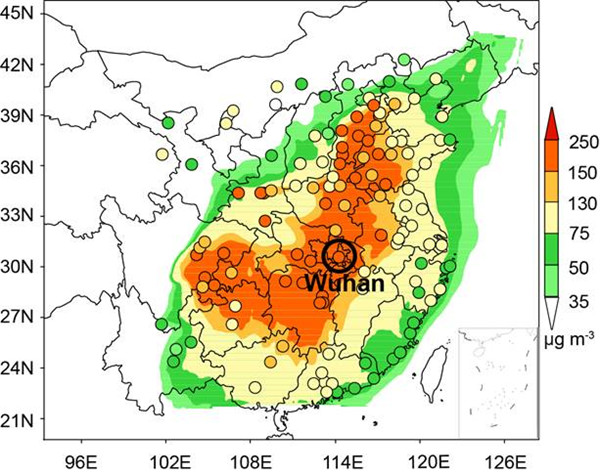
我国中东部地区在冬季经常发生区域性大气重污染过程,大范围区域灰霾与城市间灰霾的关联一直是我国大气污染领域重点关注的问题。卢苗苗博士和唐晓副研究员等在“Investigating the Transport Mechanism of PM2.5 Pollution during January 2014 in Wuhan, Central China”的文章中,分析了中部地区特大城市武汉在2014年...
近日,中国科学技术大学化学与材料科学学院及能源材料协同中心曾晓成教授(千人计划B获得者,美国内布拉斯加大学林肯分校Ameritas大学讲座教授)和美国化学学会前主席Joseph Francisco院士研究组(组员包括李磊,科大0514校友;朱重钦 博士,科大0614校友),通过第一性原理分子动力学模拟研究发现了硫酸氢铵在大气中一种全新的形成机制。成果作为通讯文章发表在《美国化学...
青岛大气中HNO3、HNO2、NH3及PM2.5中氮组分的浓度特征和气-粒平衡关系
硝酸气体 亚硝酸气体 氨气
2014/12/20
研究PM2.5中NO3-、NO2-、NH4+及其气态前体物HNO3、HNO2、NH3的浓度特征和气-粒平衡关系,对深入认识PM2.5的来源及控制因素具有重要意义.因此,本文利用2012年6—7月在青岛采集的denuder和PM2.5大气样品,分析了其中气态和颗粒态氮组分的浓度.结果发现,青岛大气中HNO3、HNO2和NH3浓度分别为(0.80±0.79) μg·m-3、(0.49±0.59) μg...
Quantification of PM2.5 organic carbon sampling artifacts in US networks
PM2.5 organic carbon sampling artifacts US networks
2010/8/13
Field blanks (bQF) and backup filters (quartz-fiber behind quartz-fiber filter; QBQ) have been adopted by US long-term air quality monitoring networks to estimate PM2.5 organic carbon (OC) sampling ar...
Organic nitrogen in PM2.5 aerosol at a forest site in the Southeast US
Organic nitrogen PM2.5 aerosol forest site Southeast US
2010/3/5
There is growing evidence that organo-nitrogen compounds may constitute a significant fraction of the aerosol nitrogen (N) budget. However, very little is known about the abundance and origin of this ...
Inverse modeling and mapping US air quality influences of inorganic PM2.5 precursor emissions using the adjoint of GEOS-Chem
US air quality influences inorganic PM2.5 precursor emissions GEOS-Chem
2009/8/25
Influences of specific sources of inorganic PM2.5 on peak and ambient aerosol concentrations in the US are evaluated using a combination of inverse modeling and sensitivity analysis. First, sulfate an...
Elemental content of PM2.5 aerosol particles collected in Göteborg during the Göte-2005 campaign in February 2005
Elemental content PM2.5 aerosol particles Gö te-2005 campaign
2009/5/7
The Göte–2005 measurement campaign aimed at studying the influence of the winter thermal inversions on urban air pollution. Elemental speciation of PM2.5 aerosol particles, collected on Teflon fi...
To what extent can aerosol water explain the discrepancy between model calculated and gravimetric PM10 and PM2.5?
extent can aerosol water PM10 PM2.5
2009/2/6
Inter-comparisons of European air quality models show that regional transport models, including the EMEP (Co-operative Programme for monitoring and evaluation of the long-range transmission of air pol...
Sensitivity of PM2.5 to climate in the Eastern US: a modeling case study
PM2.5 climate Eastern US modeling case
2008/12/17
The individual effects of various meteorological parameters on PM2.5 concentrations in the Eastern US are examined using the PMCAMx chemical transport model so that these effects and their relative ma...

